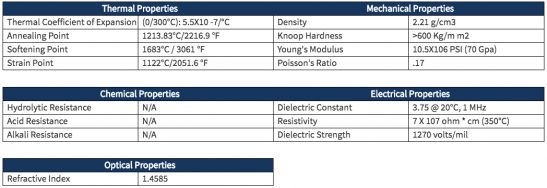
- 产品
- 厂商
热门产品
热门厂家
满足行业内人士的各种需求
如果您想选产品
-
数据手册
30万条产品数据手册,免费获取。
-
产品选型
500个细分类别,多维度指标筛选,高效选型。
如果您想卖产品
-
精准匹配
产品级搜索引擎优化,每天2000+访客为您精准匹配。
-
客户分析
内置仪表盘进行流量数据分析,了解潜在客户画像。
如果您想买产品
-
渠道正规
收录3000+全球光电厂商的产品信息,正品渠道,保障质量。
-
交易便捷
代客户采购,解决采购过程中有关付款、物流等交易障碍。
联系我们获取服务
周刊订阅
定期发布特色产品、技术资料、前沿动态等
您的邮箱将仅用于周刊推送且随时可退订
平台资讯
查看更多-
 半导体激光效率革新:突破传统,赋能工业与科研新未来
半导体激光效率革新:突破传统,赋能工业与科研新未来
全球能源转型与智能制造推动高效激光技术发展,2023 年半导体激光器市场规模预计突破 50 亿美元,年增 15%。高功率、窄线宽 976nm 激光管以低能耗、高精度成为光纤通信、医疗等领域刚需。
-
 激光器及应用:光谱技术革新,解锁物质分析新维度
激光器及应用:光谱技术革新,解锁物质分析新维度
环境污染监测、食品安全检测等领域对高精度物质分析需求激增,783nm SLM 激光器成光谱仪激发源,提供高效解决方案。
-
 激光器功率大小是怎样控制的?高精度测量设备助力精准调控
激光器功率大小是怎样控制的?高精度测量设备助力精准调控
激光技术应用广泛,激光器功率精准控制至关重要。想知道功率如何控制、怎样确保输出稳定精准?来一探究竟!
部分服务用户