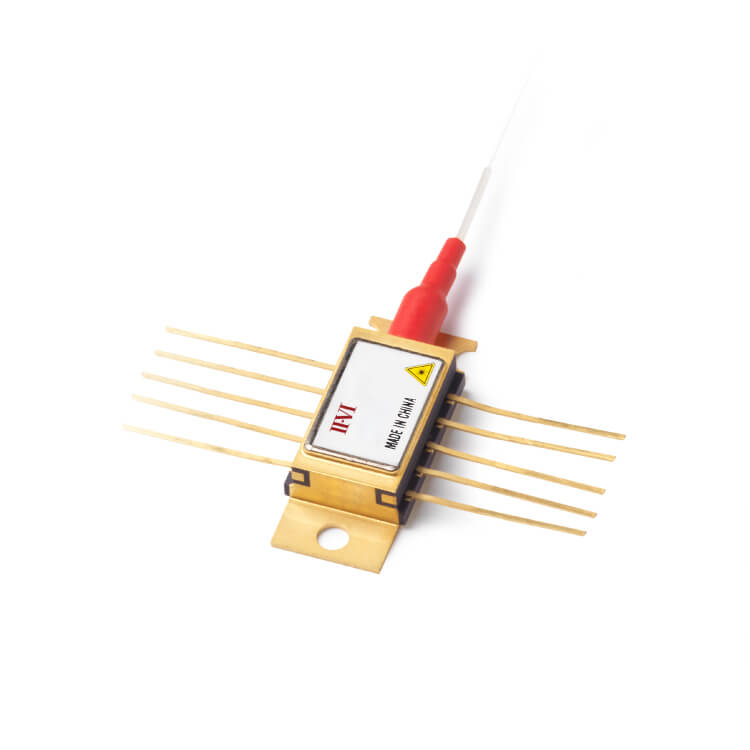
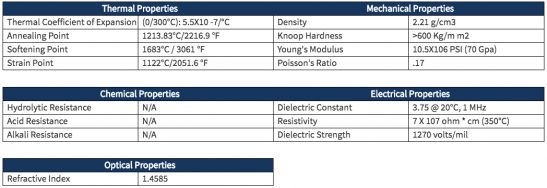
- 产品
- 厂商
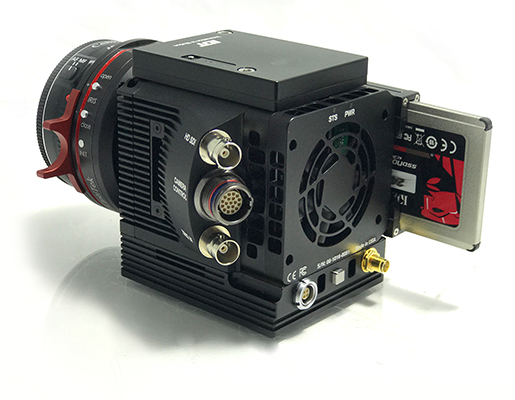
热门产品
热门厂家
满足行业内人士的各种需求
如果您想选产品
-
数据手册
30万条产品数据手册,免费获取。
-
产品选型
500个细分类别,多维度指标筛选,高效选型。
如果您想卖产品
-
精准匹配
产品级搜索引擎优化,每天2000+访客为您精准匹配。
-
客户分析
内置仪表盘进行流量数据分析,了解潜在客户画像。
如果您想买产品
-
渠道正规
收录3000+全球光电厂商的产品信息,正品渠道,保障质量。
-
交易便捷
代客户采购,解决采购过程中有关付款、物流等交易障碍。
联系我们获取服务
周刊订阅
定期发布特色产品、技术资料、前沿动态等
您的邮箱将仅用于周刊推送且随时可退订
平台资讯
查看更多-
 半导体激光器件:蓝光技术的核心驱动力与应用革新
半导体激光器件:蓝光技术的核心驱动力与应用革新
元宇宙时代,半导体激光器成为虚实交互的关键光学组件。欧司朗PLPT5 447KA蓝光激光二极管凭借高功率和小型化优势,正在推动AR/VR和投影显示技术的突破性发展,重塑下一代视觉体验。
-
 光电探测器故障重码怎么解决?专业方案助您高效排查问题
光电探测器故障重码怎么解决?专业方案助您高效排查问题
光电探测器故障重码困扰用户?本文深度解析信号失真根源,提供快速排障指南,并推荐Thorlabs FD05D高性能探测器——800-2600nm宽光谱响应、17ns超快速度,有效提升系统稳定性,解决工业检测与通信中的光信号转换难题。
-
 半导体激光器作用?揭秘795nm高功率激光器的核心应用与技术优势
半导体激光器作用?揭秘795nm高功率激光器的核心应用与技术优势
半导体激光器在量子通信、原子钟校准等尖端领域发挥关键作用。本文解析其工作原理与前沿应用,并重点推介Photodigm PH795DBR系列795nm高功率单频激光器,展现其突破性技术优势。
部分服务用户